Hello Docker
I decided to use Docker to manage my development environments (I use Ubuntu 20.04.02 LTS.).
Installing Docker on Ubuntu
- Type the following commands in your terminal to install Docker.
1. Set up the repository
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https
$ sudo apt-get install -y ca-certificates
$ sudo apt-get install -y curl
$ sudo apt-get install -y gnupg-agent
$ sudo apt-get install -y software-properties-common
$ curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
$ sudo apt-key fingerprint 0EBFCD88
$ sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable"
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
2. Install docker engine -community
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
3. usermod
- To run docker without typing
sudo,
$ sudo usermode -aG docker $USER
- This requires reboot of your system.
Installing Nvidia Docker
- Nvidia Docker should be installed to use a GPU (infrastructure) in your system, because Docker is separated with the OS.
- Nvidia driver need to be installed on your system prior to install Nvidia Docker. This can be checked at Settings > Software & Updates.
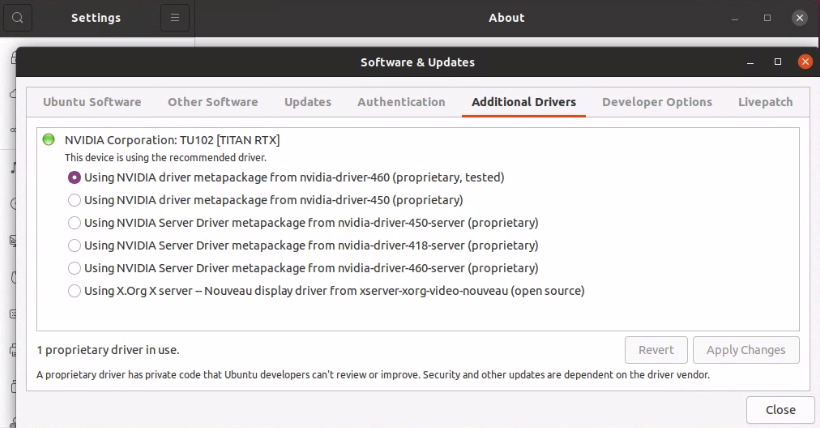
- Nvidia-Docker can be installed using the following commands
$ distribution=$(. /etc/os-release;echo $ID$VERSION_ID)
$ curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/nvidia-docker/gpgkey | sudo apt-key add -
$ curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/nvidia-docker/$distribution/nvidia-docker.list | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nvidia-docker.list
$ sudo apt-get update & sudo apt-get install -y nvidia-container-toolkit
$ sudo systemctl restart docker
Building a Pytorch container
1. Downloading an image
- Pytorch containers, built by many users, can be pulled to your system.
- Docker containers are uploaded on docker hub.
- In my case, I pulled a pytorch with pytorch-geometric container.
$ docker pull fjvallarino/pytorch-geometric
- The following command lists the downloaded images
$ docker images
2. Building a Pytorch container and utilizing Nvidia-docker
- The first step is making a share directory, e.g.,
$ cd ~
$ mkdir share
- Now we define a container whose name is
pytorchand employ the downloaded imagefjvallarino/pytorch-geometric.~/share: a file sharable space between my OS and the container--gpus all: utilized GPUs via Nvidia docker
$ docker run -itd --name pytorch fjvallarino/pytorch-geometric -v ~/share:/root/share -p 8888:8888 --gpus all
- You can list the container
$ docker ps -a
- A container can be removed
$ docker rm [CONTAINER ID]
- You can run the container
pytorch
$ docker start pytorch
$ docker exec -it pytorch bash
- Check GPUs running
root@...:/workspace# nvidia-smi
- Run the python and test Pytorch
root@...:/workspace# python3
import torch
torch.cuda.is_available()
x = torch.rand(5.3)
- Checking the file share folder
- After running a container, current path is
workspace - The defined
sharefolder path is
- After running a container, current path is
root@ ... :/worksapce# cd ..
root@ ... :/worksapce# cd root
root@ ... :/worksapce# ls
share
- Stop the
pytorchcontainer
docker container stop pytorch
3. Install Jupyter Notebook on a container
I am very happy to say docker supports Anaconda and we don’t need to install on a container. And jupyter notebook can be installed.
conda install jupyter
And start jupyter notebook
jupyter notebook --ip=0.0.0.0 --port=8888 --allow-root
Other approach is using VSCODE
References
- Pytorch and Jupyternotebook on Docker (in Korean)
- Getting started Docker (in Korean)
Future plan
- Upload my IMGs